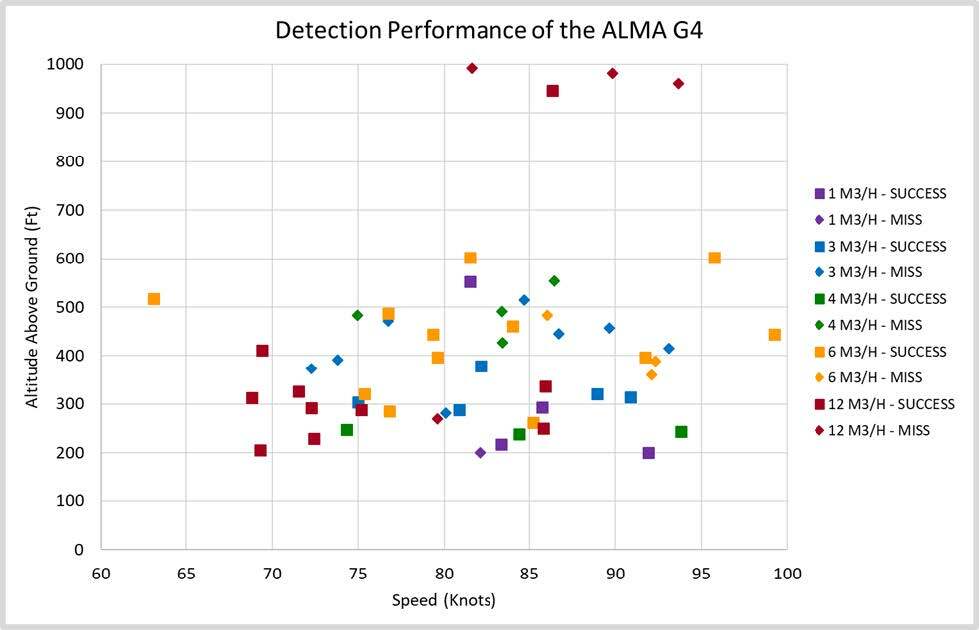
The ALMA G4 mounted on the fixed-wing Maule aircraft used during the demonstration can, with high reliability, detect gas leaks with flow rates greater than 6 cubic meters per hour from 600 feet above the ground. The ALMA G4 mounted on the fixed-wing Maule aircraft can detect smaller flow rates with high reliability from lower altitudes. A fixed-wing aircraft has less ability to aim the laser beam to the specified 5 to 20 meters downwind as compared to a helicopter. Because of this, the ability to consistently detect tiny plumes of methane is less repeatable when using the Maule fixed-wing aircraft as compared to the helicopter-based inspections. The results of all the testing are depicted in the chart below.
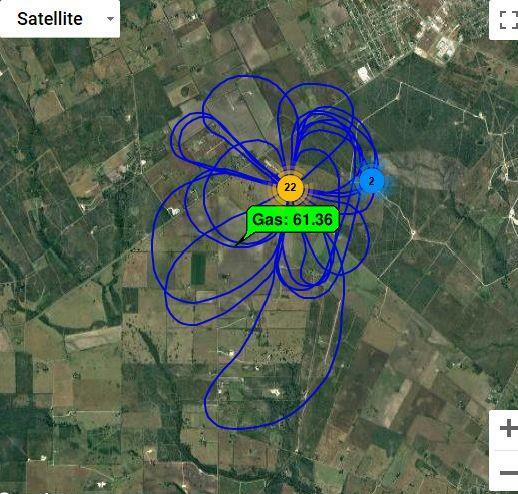
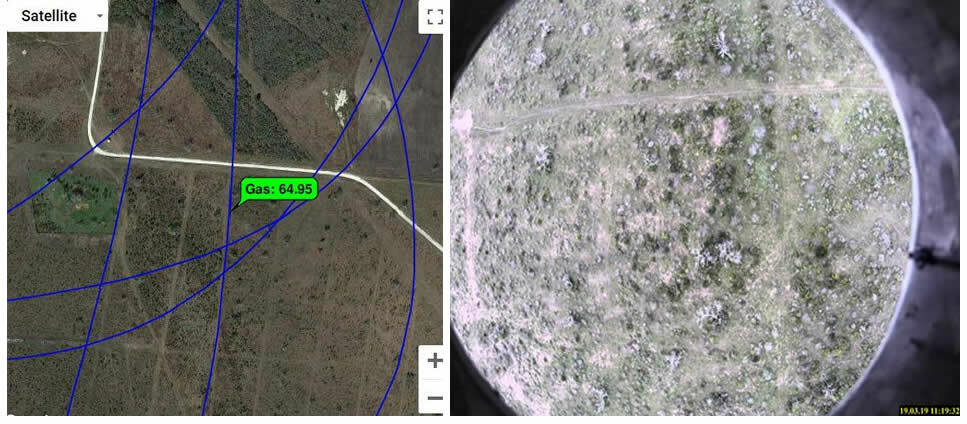
The ALMA G4 gas leak detector repeatedly detected an unknown methane source when performing 180° turns to head back to the artificial leak. The source of the methane is under investigation.
Pergam ALMA G4 Mini
The Pergam ALMA G4 Mini is a precision optical instrument for detection of increased methane gas concentrations in ambient air (the gas cloud from a pipeline leak or other source) from helicopters.ALMA G4 Mini is based on an infrared laser emitting a wavelength which methane gas absorbs. The system analyzes the laser light backscatter reflected from the ground to determine how much if any of the laser energy was absorbed by the methane in natural gas. A unique detection algorithm allows for real-time measurement of total methane content along the laser light path to the ground. The system compensates for atmospheric methane using a laser rangefinder and advanced algorithms. The operator interface displays real-time detection alerts, logging visual observation details, controls and monitors system operation, and manages data and video storage. The system continually records all inspection data including GPS location which is reviewed post inspection to generate a report.
Technical Details

Pictures of ALMA G4 Installed on MAULE Airplane



Using ALMA’s Gas Detection Report to Find the Gas Source
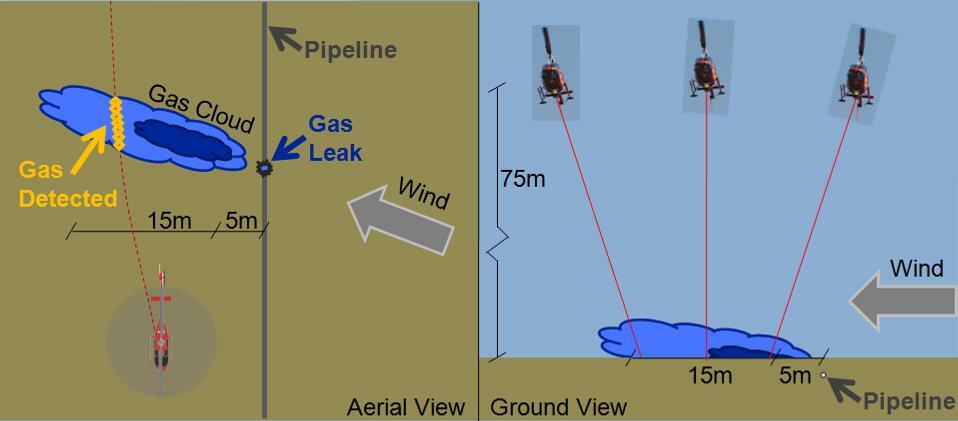
- The ALMA equipment detects the gas cloud coming from the leak in the pipeline, not the leak itself. See diagram.
- ALMA’s laser must pass downwind of the pipeline to detect the gas cloud.
- ALMA can detect methane gas coming from other sources than the pipeline such as animals, farms, cars/trucks, etc…
Information in Report for Each Gas Detection (Potential Gas Leak)
- Gas detection information including GPS coordinates, size, etc…
- Map with gas detection location
- Pictures of where gas was detected
How to Find Gas Source
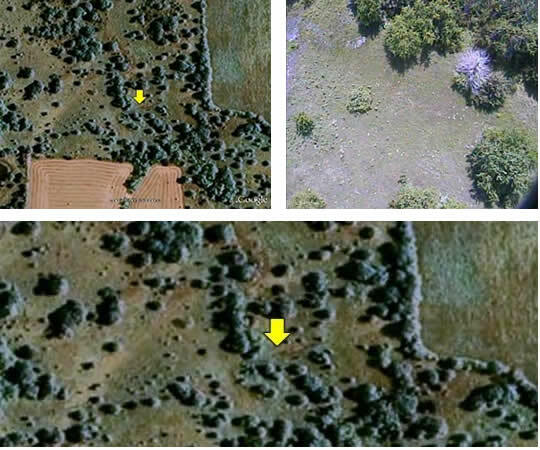
- Step 1: Go to gas detection location per GPS coordinates or map, and picture
- Step 2: Search for the Source of the Gas. The location from step 1 is where the gas was detected at that particular date, time, and wind. Walk to the pipeline and inspect the area around the pipeline in both directions as illustrated by the orange oval. Remember ALMA can detect methane gas coming from other sources such as animals, farms, cars/trucks, etc…
Understanding PPM*M
Parts Per Million has no units such as cubic feet or cubic meters. The laser in Pergam’s systems measure Parts Per Million along its path to the ground so must have a distance unit which is, in this case, a meter (M) resulting in PPM*M.Natural Gas Detections Detailed Information
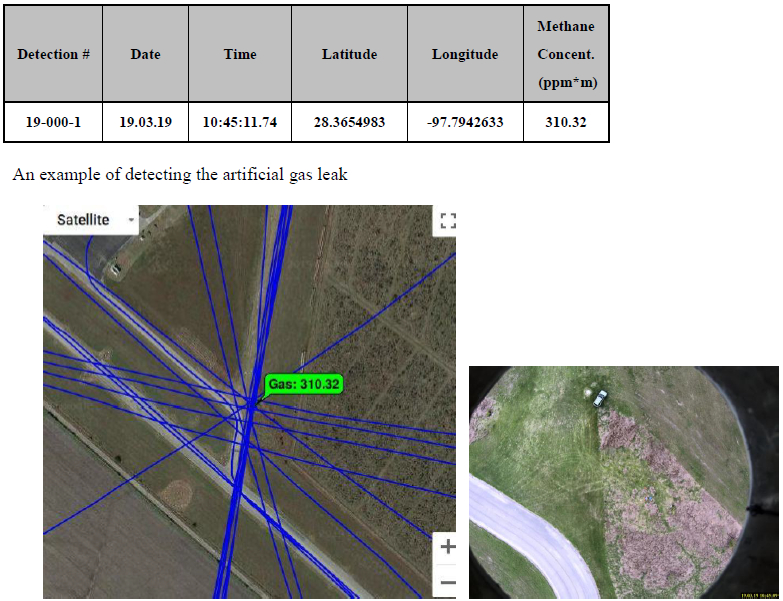
The ALMA G4 repeatedly detected an unknown methane source when performing 180° turns to head back to the artificial leak. The source of the methane is under investigation.
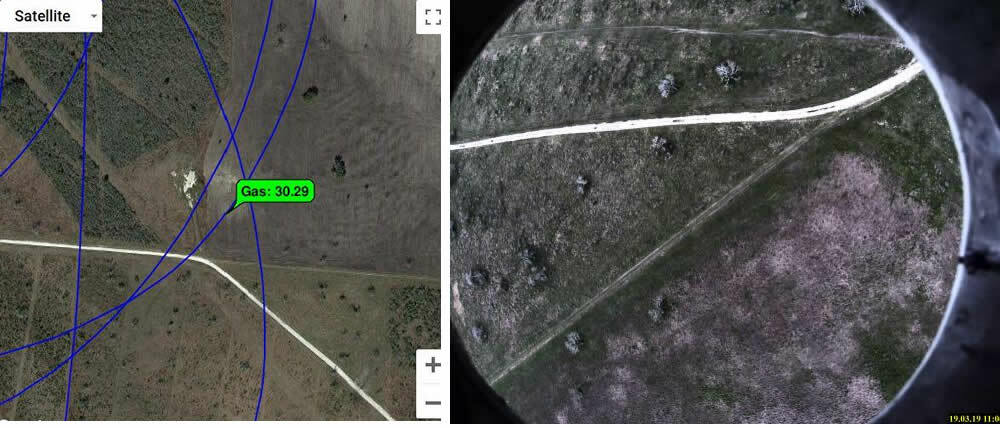

The ALMA G4 repeatedly detected an unknown methane source when performing 180° turns to head back to the artificial leak. The source of the methane is under investigation.